Table of contents
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a powerful methodology that emphasizes writing tests before implementing code, ensuring a more robust and error-resistant software development process. In this blog post, we’ll explore how to implement TDD in Ruby on a Kali Linux system, providing step-by-step guidance for setting up your environment and writing effective tests.
Prerequisites:
Install Ruby*:* Ensure that Ruby is installed on your Kali Linux system. You can use the following command to install Ruby:
sudo apt-get install ruby-fullCreate a new Ruby project: Set up a new directory for your Ruby project. Navigate to the project directory in the terminal.
mkdir gamecd gameFor Simple Test:
Create a ruby file named “game.rb”.
touch game.rbOpen file using Vim.
vim game.rbPaste this code then,
class RockPaperScissors def play(player1, player2) if (player1 == "rock" && player2 == "scissors" || player1 == "scissors" && player2 == "paper" || player1 == "paper" && player2 == "rock") 'Player 1 Wins' elsif(player1 == player2) 'Tie' else 'Player 2 Wins' end end endCtrl+C:wq!Create test file named “game_test.rb”
touch game_test.rbOpen test file
vim game_test.rbPaste this code
require_relative 'game.rb' require 'minitest/autorun' describe "RockPaperScissors" do it "returns 'Player 1 Wins' when rock vs scissors" do # Assemble # Action result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("rock", "scissors") # Assert assert_equal('Player 1 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 1 Wins' when scissors vs paper" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("scissors", "paper") assert_equal('Player 1 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 1 Wins' when paper vs rock" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("paper", "rock") assert_equal('Player 1 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 2 Wins' when scissors vs rock" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("scissors", "rock") assert_equal('Player 2 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 2 Wins' when paper vs scissors" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("paper", "scissors") assert_equal('Player 2 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Player 2 Wins' when rock vs paper" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("rock", "paper") assert_equal('Player 2 Wins', result) end it "returns 'Tie' when scissors vs scissors" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("scissors", "scissors") assert_equal('Tie', result) end it "returns 'Tie' when paper vs paper" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("paper", "paper") assert_equal('Tie', result) end it "returns 'Tie' when rock vs rock" do result = RockPaperScissors.new.play("rock", "rock") assert_equal('Tie', result) end endCtrl+C:wq!Run the game_test.rb file
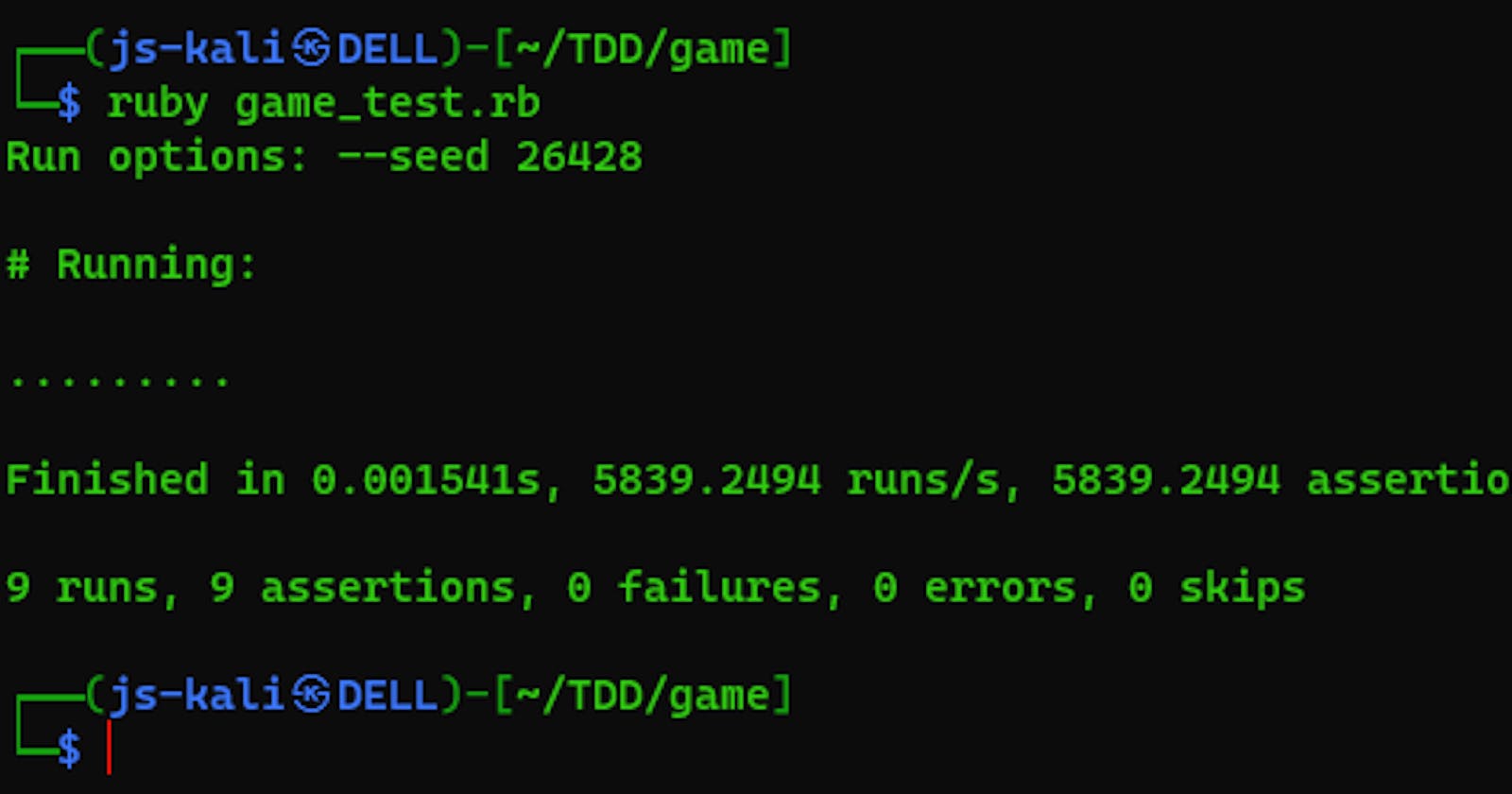
ruby game_test.rb
Conclusion: Test-Driven Development with Minitest in Ruby on a Kali Linux system provides a lightweight yet effective approach to writing reliable code. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can establish a TDD workflow for your Ruby projects using Minitest. Happy testing and coding!